一个注解实现接口幂等性
一、什么是幂等性?
二、哪些请求天生就是幂等的?
举一个简单的例子
update table set a = a + 1 where v = 1这样的更新就非幂等了。三、为什么需要幂等
1.超时重试
2.异步回调
3.消息队列
四、实现幂等的关键因素
关键因素1
关键因素2
五、注解实现幂等性
https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice
1.自定义注解
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(value = ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface Idempotent { /** * 参数名,表示将从哪个参数中获取属性值。 * 获取到的属性值将作为KEY。 * * @return */ String name() default ""; /** * 属性,表示将获取哪个属性的值。 * * @return */ String field() default ""; /** * 参数类型 * * @return */ Class type();}
2.统一的请求入参对象
@Datapublic class RequestData<T> { private Header header; private T body;}@Datapublic class Header { private String token;}@Datapublic class Order { String orderNo;}
3.AOP处理
import com.springboot.micrometer.annotation.Idempotent;import com.springboot.micrometer.entity.RequestData;import com.springboot.micrometer.idempotent.RedisIdempotentStorage;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.util.Map;@Aspect@Componentpublic class IdempotentAspect { @Resource private RedisIdempotentStorage redisIdempotentStorage; @Pointcut("@annotation(com.springboot.micrometer.annotation.Idempotent)") public void idempotent() { } @Around("idempotent()") public Object methodAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable { MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); Idempotent idempotent = method.getAnnotation(Idempotent.class); String field = idempotent.field(); String name = idempotent.name(); Class clazzType = idempotent.type(); String token = ""; Object object = clazzType.newInstance(); Map<String, Object> paramValue = AopUtils.getParamValue(joinPoint); if (object instanceof RequestData) { RequestData idempotentEntity = (RequestData) paramValue.get(name); token = String.valueOf(AopUtils.getFieldValue(idempotentEntity.getHeader(), field)); } if (redisIdempotentStorage.delete(token)) { return joinPoint.proceed(); } return "重复请求"; }}import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.CodeSignature;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class AopUtils { public static Object getFieldValue(Object obj, String name) throws Exception { Field[] fields = obj.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); Object object = null; for (Field field : fields) { field.setAccessible(true); if (field.getName().toUpperCase().equals(name.toUpperCase())) { object = field.get(obj); break; } } return object; } public static Map<String, Object> getParamValue(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) { Object[] paramValues = joinPoint.getArgs(); String[] paramNames = ((CodeSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getParameterNames(); Map<String, Object> param = new HashMap<>(paramNames.length); for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) { param.put(paramNames[i], paramValues[i]); } return param; }}
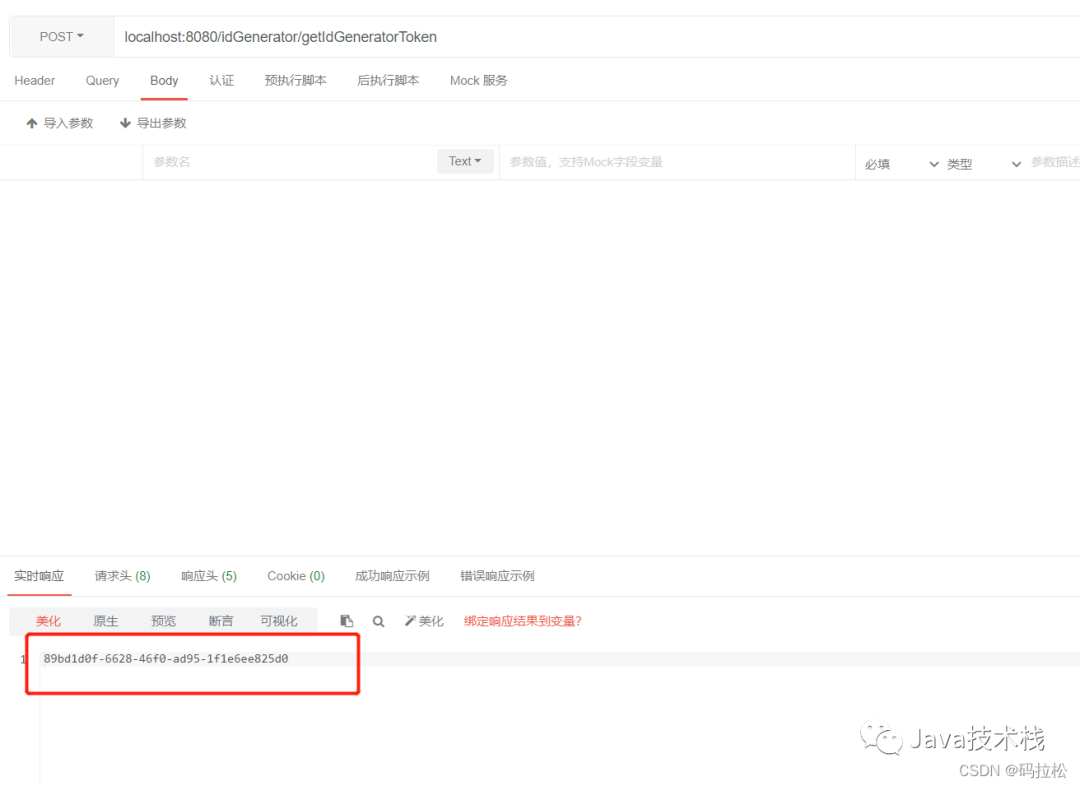
4.Token值生成
import com.springboot.micrometer.idempotent.RedisIdempotentStorage;import com.springboot.micrometer.util.IdGeneratorUtil;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import javax.annotation.Resource;@RestController@RequestMapping("/idGenerator")public class IdGeneratorController { @Resource private RedisIdempotentStorage redisIdempotentStorage; @RequestMapping("/getIdGeneratorToken") public String getIdGeneratorToken() { String generateId = IdGeneratorUtil.generateId(); redisIdempotentStorage.save(generateId); return generateId; }}public interface IdempotentStorage { void save(String idempotentId); boolean delete(String idempotentId);}import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.annotation.Resource;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Componentpublic class RedisIdempotentStorage implements IdempotentStorage { @Resource private RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> redisTemplate; @Override public void save(String idempotentId) { redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(idempotentId, idempotentId, 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES); } @Override public boolean delete(String idempotentId) { return redisTemplate.delete(idempotentId); }}import java.util.UUID;public class IdGeneratorUtil { public static String generateId() { return UUID.randomUUID().toString(); }}
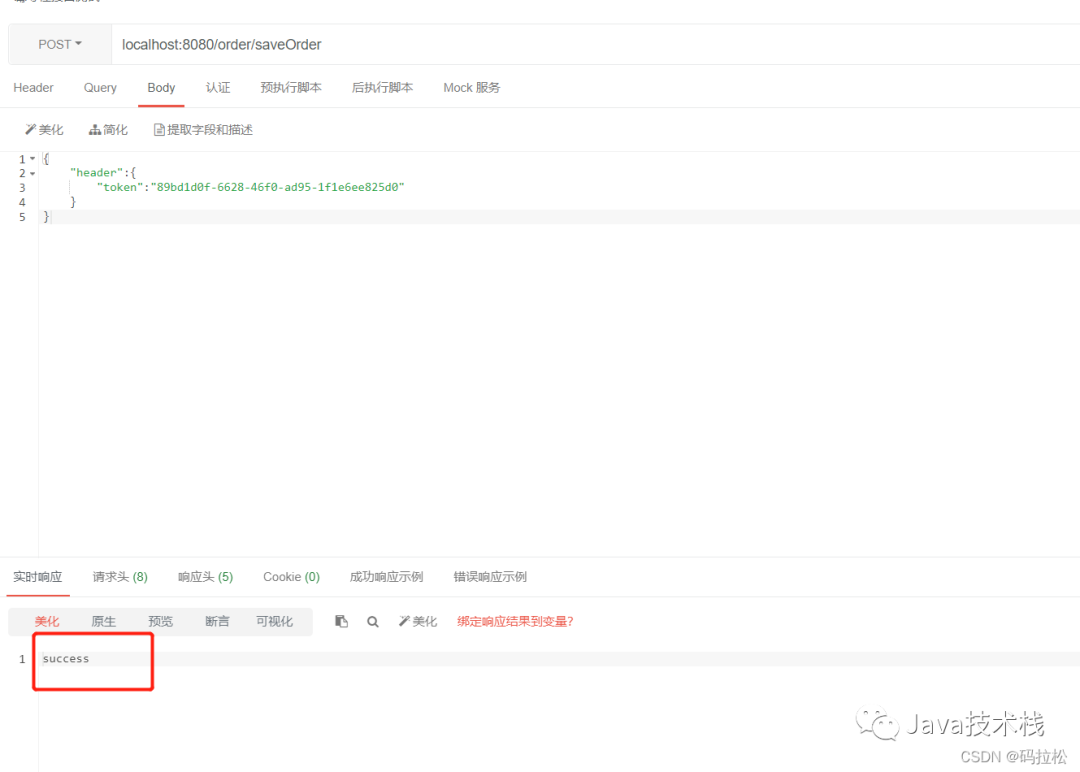
5. 请求示例
import com.springboot.micrometer.annotation.Idempotent;import com.springboot.micrometer.entity.Order;import com.springboot.micrometer.entity.RequestData;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;@RestController@RequestMapping("/order")public class OrderController { @RequestMapping("/saveOrder") @Idempotent(name = "requestData", type = RequestData.class, field = "token") public String saveOrder(@RequestBody RequestData<Order> requestData) { return "success"; }}

 微信赞赏
微信赞赏 支付宝扫码领红包
支付宝扫码领红包