详解Java lambda表达式

本文的脉络
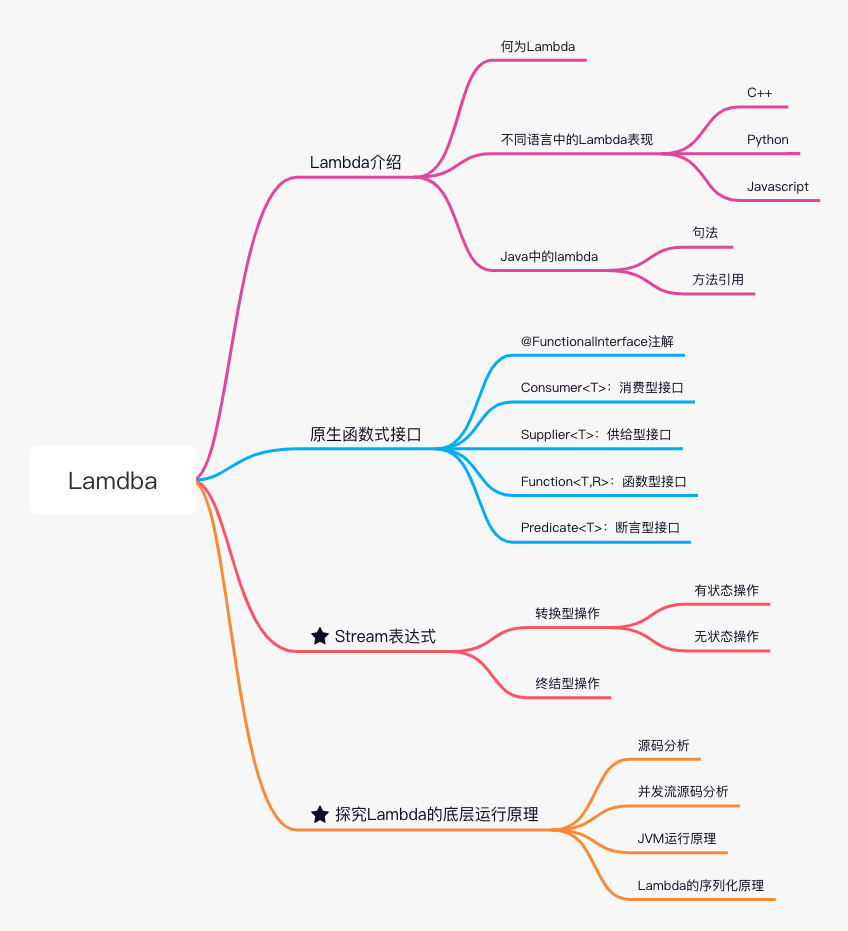
Lambda介绍
何为lambda
匿名函数(英语:Anonymous Function)在计算机编程中是指一类无需定义标识符(函数名)的函数或子程序。
不同语言中的Lambda
Python
add2 = lambda x,y:x+yprint add2(1,2) #3sum2 = lambda x,y=10:x+yprint sum2(1) #11print sum2(1,100) #101
C++
[ capture clause ] (parameters) -> return-type{definition of method}
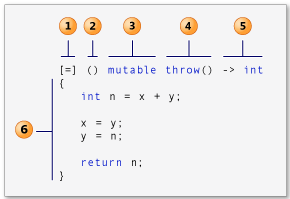
[1]:Lambda表达式的引入标志,在‘[]’里面可以填入‘=’或‘&’表示该lambda表达式“捕获”(lambda表达式在一定的scope可以访问的数据)的数据时以什么方式捕获的,‘&’表示一引用的方式;‘=’表明以值传递的方式捕获,除非专门指出。
[2]:Lambda表达式的参数列表
[3]:Mutable 标识
[4]:异常标识
[5]:返回值
void func(std::vector<int>& v) {std::for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), [](int i) {cout << i << endl;});}
Javascript
(p1 [,p2,p3,....pn]) => { code block }let func = x => x * x;func(2) #4
Java Lambda 表达式
句法
() -> System.out.println("零参数 lambda");p -> System.out.println("一个参数:" + p);(p1 [,p2,p3,....pn]) -> System.out.println("多个参数:" + p1 + ", " + p2 + ... + pn);(parameter1, parameter2) -> { code block [return] }方法引用
Consumer<String> c = [ (s) -> System.out.println(s); <=> System.out::println; ]List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList();Consumer<String> c = [ (e) => list.add(e); <=> list::add; ]
Supplier<List<String>> s = [ () -> new ArrayList<>(); <=> ArrayList::new; ]原生函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface注解
Consumer: 消费性接口
public interface Consumer<T> {void accept(T t);}
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6");list.foreach(System.out::println); //打印数组
Supplier: 供给型接口
public interface Supplier<T> {T get();}
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6");List<String> newList = list.stream().filter(x -> x >= 2).collect(Collectors.toList());// 将大于等于2的数重新收集成一个集合,其中Collectors.toList()的函数原型为// new CollectorImpl<>((Supplier<List<T>>) ArrayList::new, List::add,(left, right) -> { left.addAll(right); return left; },CH_ID)// 原型中的ArrayList::new即为Supplier类型
Function: 函数型接口
public interface Function<T, R> {R apply(T t);}
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6");List<Integet> newList = list.stream().map(Integer::parseInt).collect(Collectors.toList());// map将list中所有的元素的类型由 String 通过 Integer.parseInt的方式转换为Intger。简单来说就是A => B;
Predicate: 断言型接口
public interface Predicate<T> {boolean test(T t);}
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6");List<String> newList = list.stream().filter(x -> x >= 2).collect(Collectors.toList());// 将大于等于2的数重新收集成一个集合,filter中的 x -> x >= 2就是Predicate接口
Stream表达式
其中Stream的操作大致分为两类
-
中间型操作 -
终结型操作
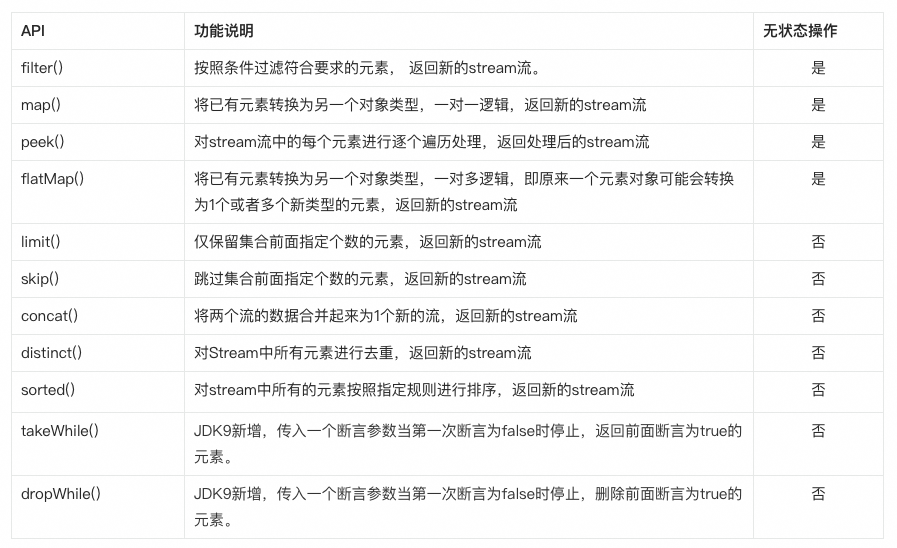
中间型操作
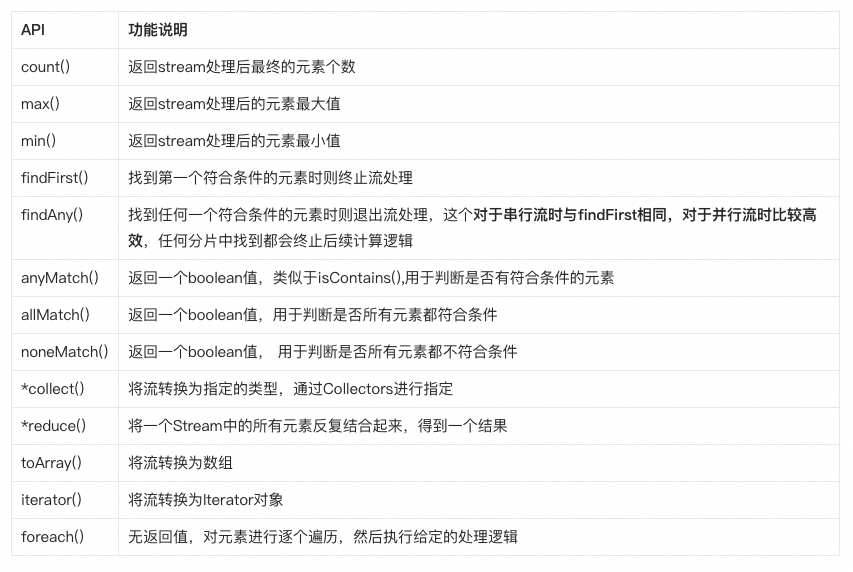
终结型操作
探究lambda运行的底层原理
源码分析
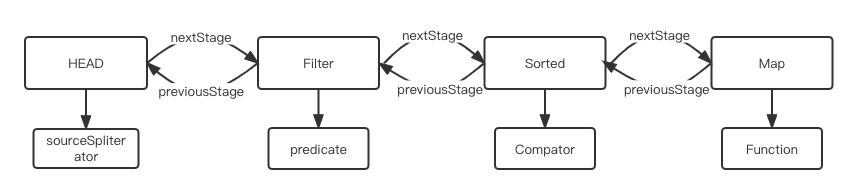
Set<Integer> collect = list.stream().filter(e -> e > 2).sorted().map(e -> e * 2).collect(Collectors.toSet());上诉例子可拆解成下面5部分:Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream();Stream<Integer> filterStream = stream.filter(e -> e > 2);Stream<Integer> sortedStream = filterStream.sorted();Stream<Integer> mapStream = sortedStream.map(e -> e * 2);Set<Integer> integers = mapStream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
-
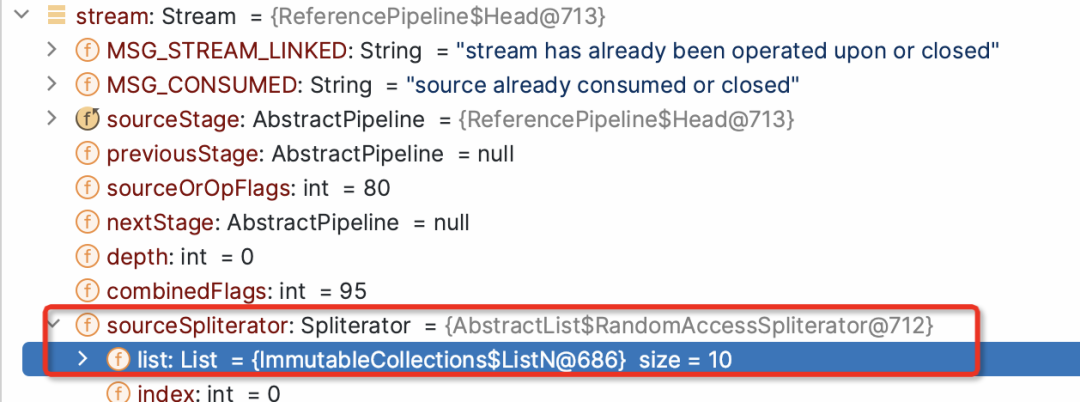
list.stream()
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);}default Stream<E> stream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}
public static <T> Stream<T> stream(Spliterator<T> spliterator, boolean parallel) {Objects.requireNonNull(spliterator);return new ReferencePipeline.Head<>(spliterator,StreamOpFlag.fromCharacteristics(spliterator),parallel);}
-
stream.filter(e -> e > 2)
public final Stream<P_OUT> filter(Predicate<? super P_OUT> predicate) {Objects.requireNonNull(predicate);return new StatelessOp<P_OUT, P_OUT>(this, StreamShape.REFERENCE,StreamOpFlag.NOT_SIZED) {Sink<P_OUT> opWrapSink(int flags, Sink<P_OUT> sink) {return new Sink.ChainedReference<P_OUT, P_OUT>(sink) {public void begin(long size) {downstream.begin(-1);}public void accept(P_OUT u) {if (predicate.test(u))downstream.accept(u);}};}};}
abstract static class StatelessOp<E_IN, E_OUT>extends ReferencePipeline<E_IN, E_OUT> {StatelessOp(AbstractPipeline<?, E_IN, ?> upstream,StreamShape inputShape,int opFlags) {super(upstream, opFlags);assert upstream.getOutputShape() == inputShape;}final boolean opIsStateful() {return false;}}abstract static class StatefulOp<E_IN, E_OUT>extends ReferencePipeline<E_IN, E_OUT> {StatefulOp(AbstractPipeline<?, E_IN, ?> upstream,StreamShape inputShape,int opFlags) {super(upstream, opFlags);assert upstream.getOutputShape() == inputShape;}final boolean opIsStateful() {return true;}}
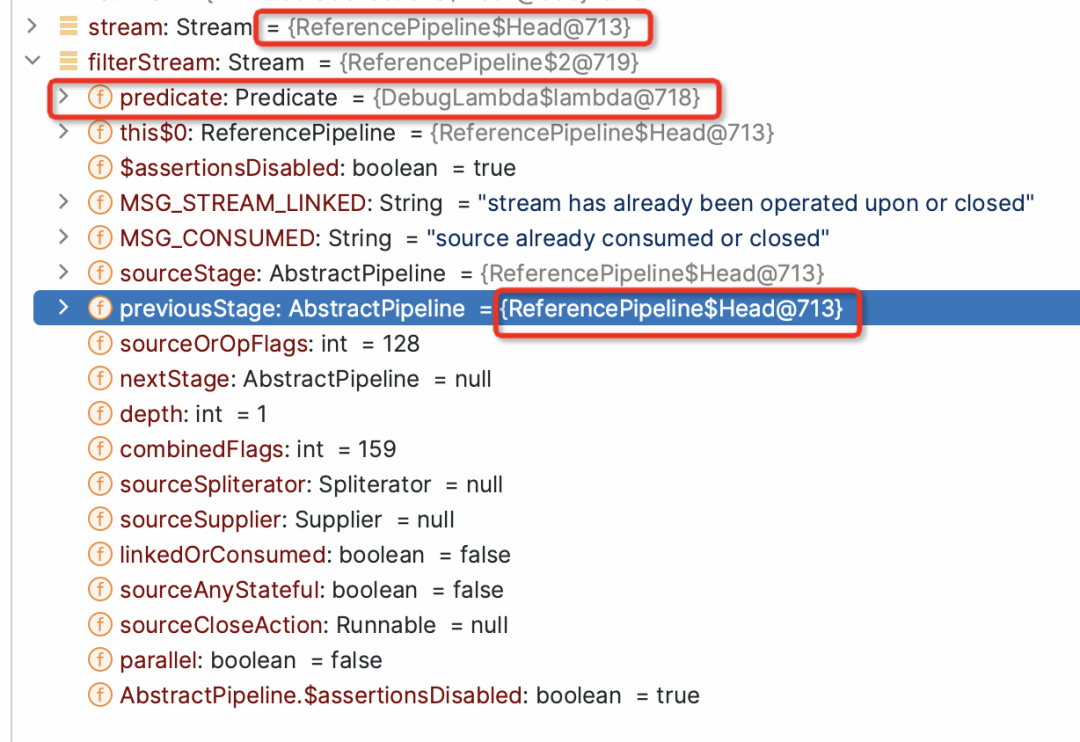
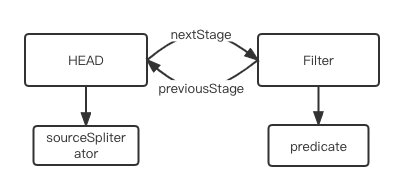
需要注意的是 filter等方法的构造方法:
new StatelessOp<P_OUT,
P_OUT>(this,StreamShape.REFERENCE,StreamOpFlag.NOT_SIZED)
AbstractPipeline(AbstractPipeline<?, E_IN, ?> previousStage, int opFlags) {if (previousStage.linkedOrConsumed)throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);previousStage.linkedOrConsumed = true; //previousStage.nextStage = this; // 注意打注释的语句this.previousStage = previousStage; //this.sourceOrOpFlags = opFlags & StreamOpFlag.OP_MASK;this.combinedFlags = StreamOpFlag.combineOpFlags(opFlags, previousStage.combinedFlags);this.sourceStage = previousStage.sourceStage;if (opIsStateful())sourceStage.sourceAnyStateful = true;this.depth = previousStage.depth + 1;}
p.next = this;this.pre = p;
-
filterStream.sorted()
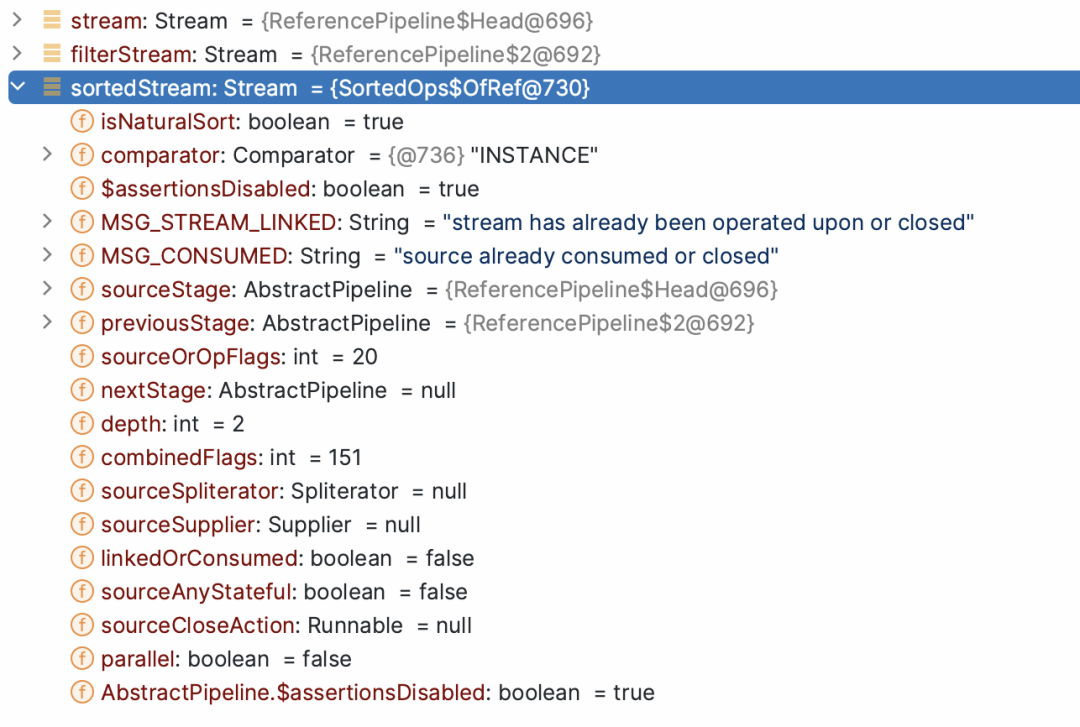
public final Stream<P_OUT> sorted() {return SortedOps.makeRef(this);}
OfRef(AbstractPipeline<?, T, ?> upstream) {super(upstream, StreamShape.REFERENCE,StreamOpFlag.IS_ORDERED | StreamOpFlag.IS_SORTED);this.isNaturalSort = true;// Will throw CCE when we try to sort if T is not ComparableComparator<? super T> comp = (Comparator<? super T>) Comparator.naturalOrder();this.comparator = comp;}
和filter操作一样,将Sorted节点加入链表中同时设置标志位:
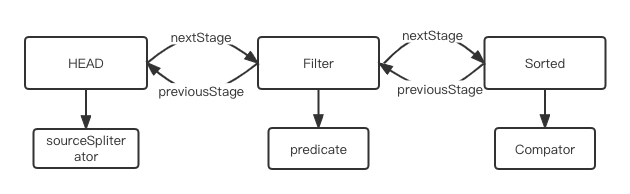
-
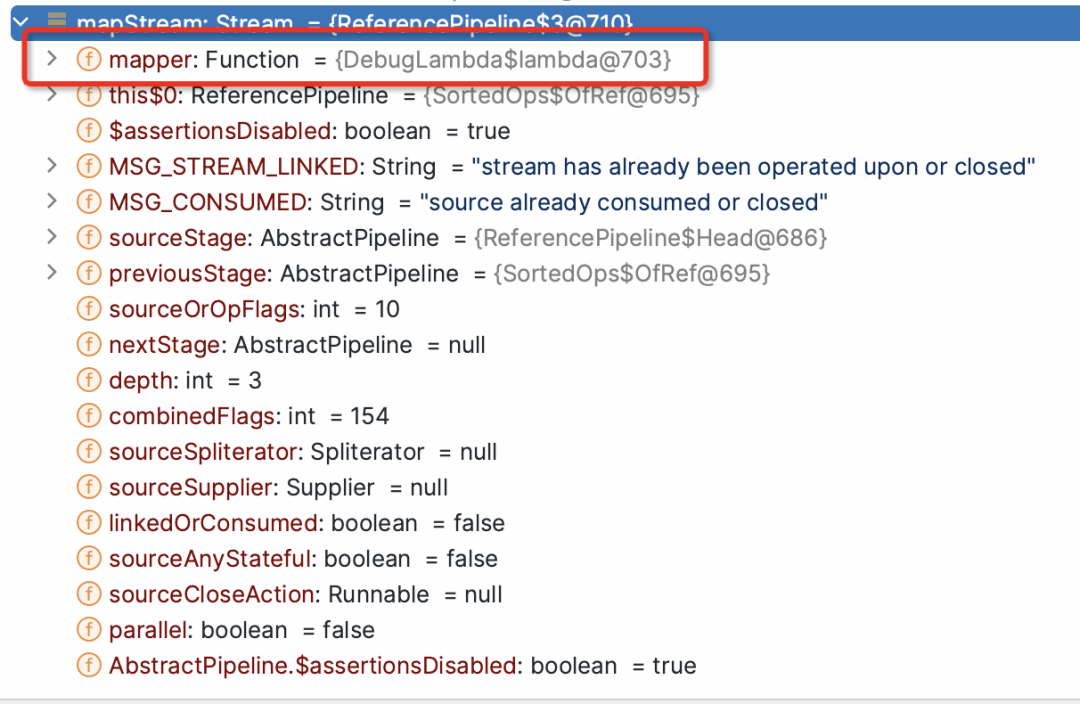
sortedStream.map(e -> e * 2)
public final <R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super P_OUT, ? extends R> mapper) {Objects.requireNonNull(mapper);return new StatelessOp<P_OUT, R>(this, StreamShape.REFERENCE,StreamOpFlag.NOT_SORTED | StreamOpFlag.NOT_DISTINCT) {Sink<P_OUT> opWrapSink(int flags, Sink<R> sink) {return new Sink.ChainedReference<P_OUT, R>(sink) {public void accept(P_OUT u) {downstream.accept(mapper.apply(u));}};}};}
-
mapStream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
public final <R, A> R collect(Collector<? super P_OUT, A, R> collector) {A container;if (isParallel()&& (collector.characteristics().contains(Collector.Characteristics.CONCURRENT))&& (!isOrdered() || collector.characteristics().contains(Collector.Characteristics.UNORDERED))) {container = collector.supplier().get();BiConsumer<A, ? super P_OUT> accumulator = collector.accumulator();forEach(u -> accumulator.accept(container, u));}else {container = evaluate(ReduceOps.makeRef(collector));}return collector.characteristics().contains(Collector.Characteristics.IDENTITY_FINISH)? (R) container: collector.finisher().apply(container);}
new CollectorImpl<>((Supplier<Set<T>>) HashSet::new, Set::add,(left, right) -> {if (left.size() < right.size()) {right.addAll(left); return right;} else {left.addAll(right); return left;}},CH_UNORDERED_ID)
public static <T, I> TerminalOp<T, I>makeRef(Collector<? super T, I, ?> collector) {Supplier<I> supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(collector).supplier();BiConsumer<I, ? super T> accumulator = collector.accumulator();BinaryOperator<I> combiner = collector.combiner();class ReducingSink extends Box<I>implements AccumulatingSink<T, I, ReducingSink> {public void begin(long size) {state = supplier.get();}public void accept(T t) {accumulator.accept(state, t);}public void combine(ReducingSink other) {state = combiner.apply(state, other.state);}}return new ReduceOp<T, I, ReducingSink>(StreamShape.REFERENCE) {public ReducingSink makeSink() {return new ReducingSink();}public int getOpFlags() {return collector.characteristics().contains(Collector.Characteristics.UNORDERED)? StreamOpFlag.NOT_ORDERED: 0;}};}
final <R> R evaluate(TerminalOp<E_OUT, R> terminalOp) {assert getOutputShape() == terminalOp.inputShape();if (linkedOrConsumed)throw new IllegalStateException(MSG_STREAM_LINKED);linkedOrConsumed = true;return isParallel()? terminalOp.evaluateParallel(this, sourceSpliterator(terminalOp.getOpFlags())): terminalOp.evaluateSequential(this, sourceSpliterator(terminalOp.getOpFlags()));}
public <P_IN> R evaluateSequential(PipelineHelper<T> helper,Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {return helper.wrapAndCopyInto(makeSink(), spliterator).get();}
final <P_IN, S extends Sink<E_OUT>> S wrapAndCopyInto(S sink, Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {copyInto(wrapSink(Objects.requireNonNull(sink)), spliterator);return sink;}
final <P_IN> void copyInto(Sink<P_IN> wrappedSink, Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {Objects.requireNonNull(wrappedSink);if (!StreamOpFlag.SHORT_CIRCUIT.isKnown(getStreamAndOpFlags())) {wrappedSink.begin(spliterator.getExactSizeIfKnown());spliterator.forEachRemaining(wrappedSink);wrappedSink.end();}else {copyIntoWithCancel(wrappedSink, spliterator);}}
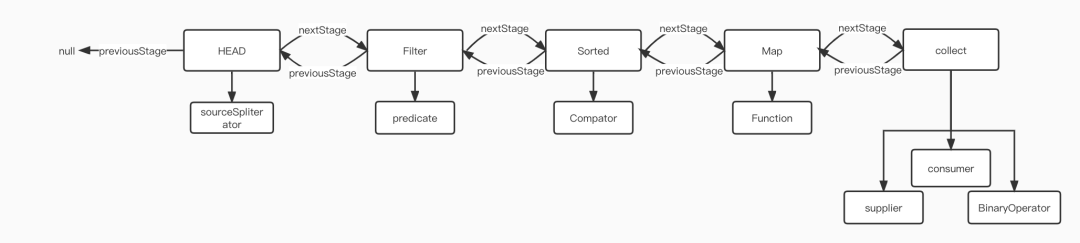

最后调用:
并发流源码分析
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);// Set<Integer> collect = list.stream()// .filter(e -> e > 2)// .filter(e -> e < 8)// .sorted()// .map(e -> e * 2)// .peek(System.out::println)// .collect(Collectors.toSet());Stream<Integer> stream = list.stream().parallel(); // list.parallelStream()Stream<Integer> filterStream = stream.filter(e -> e > 2);Stream<Integer> sortedStream = filterStream.sorted();Stream<Integer> mapStream = sortedStream.map(e -> e * 2);Set<Integer> integers = mapStream.collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(integers);}
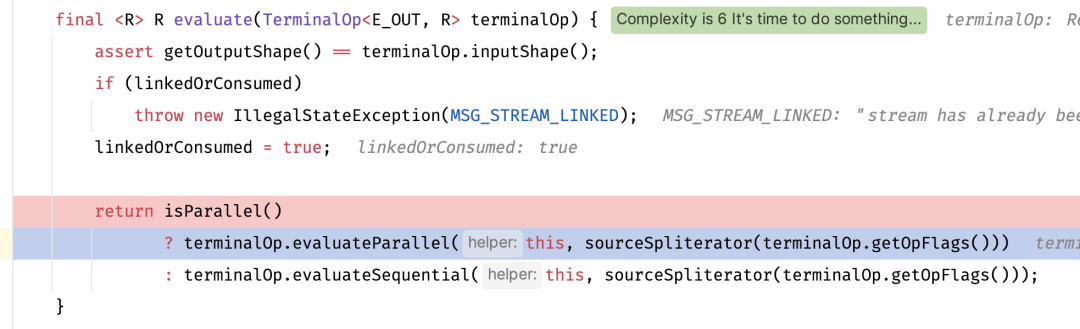
public <P_IN> R evaluateParallel(PipelineHelper<T> helper,Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {return new ReduceTask<>(this, helper, spliterator).invoke().get();}
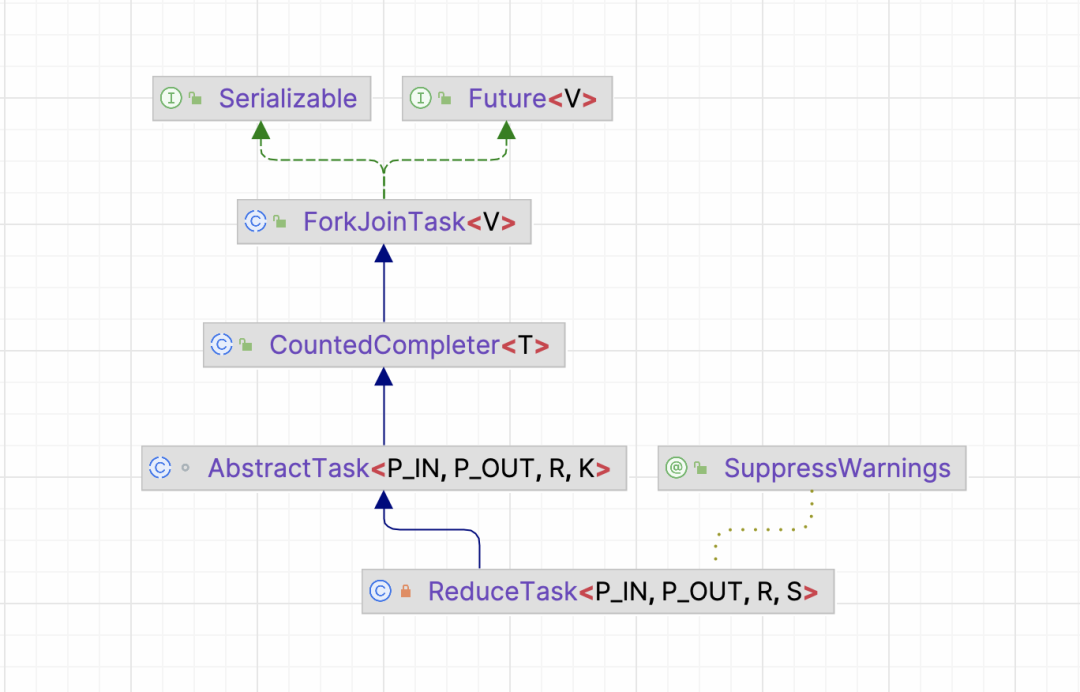
private static final class ReduceTask<P_IN, P_OUT, R,S extends AccumulatingSink<P_OUT, R, S>>extends AbstractTask<P_IN, P_OUT, S, ReduceTask<P_IN, P_OUT, R, S>> {private final ReduceOp<P_OUT, R, S> op;ReduceTask(ReduceOp<P_OUT, R, S> op,PipelineHelper<P_OUT> helper,Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {super(helper, spliterator);this.op = op;}ReduceTask(ReduceTask<P_IN, P_OUT, R, S> parent,Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {super(parent, spliterator);this.op = parent.op;}protected ReduceTask<P_IN, P_OUT, R, S> makeChild(Spliterator<P_IN> spliterator) {return new ReduceTask<>(this, spliterator);}protected S doLeaf() {return helper.wrapAndCopyInto(op.makeSink(), spliterator);}public void onCompletion(CountedCompleter<?> caller) {if (!isLeaf()) {S leftResult = leftChild.getLocalResult();leftResult.combine(rightChild.getLocalResult());setLocalResult(leftResult);}// GC spliterator, left and right childsuper.onCompletion(caller);}}
//AbstractTask extends CountedCompleterabstract class AbstractTask<P_IN, P_OUT, R,K extends AbstractTask<P_IN, P_OUT, R, K>>extends CountedCompleter<R> {}//AbstractTask extends ForkJoinTaskpublic abstract class CountedCompleter<T> extends ForkJoinTask<T> {}
public final V invoke() {int s;if (((s = doInvoke()) & ABNORMAL) != 0)reportException(s);return getRawResult();}private int doInvoke() {int s; Thread t; ForkJoinWorkerThread wt;return (s = doExec()) < 0 ? s :((t = Thread.currentThread()) instanceof ForkJoinWorkerThread) ?(wt = (ForkJoinWorkerThread)t).pool.awaitJoin(wt.workQueue, this, 0L) :externalAwaitDone();}final int doExec() {int s; boolean completed;if ((s = status) >= 0) {try {completed = exec();} catch (Throwable rex) {completed = false;s = setExceptionalCompletion(rex);}if (completed)s = setDone();}return s;}protected final boolean exec() {compute();return false;}
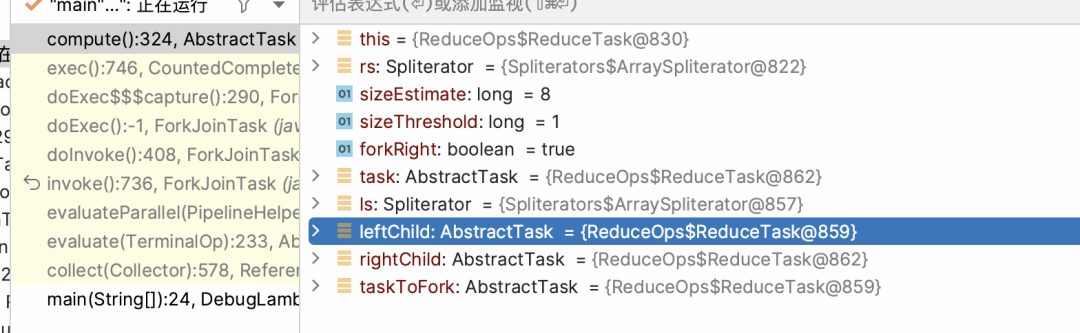
public void compute() {Spliterator<P_IN> rs = spliterator, ls; // right, left spliteratorslong sizeEstimate = rs.estimateSize();long sizeThreshold = getTargetSize(sizeEstimate);boolean forkRight = false;("unchecked") K task = (K) this;while (sizeEstimate > sizeThreshold && (ls = rs.trySplit()) != null) {K leftChild, rightChild, taskToFork;task.leftChild = leftChild = task.makeChild(ls);task.rightChild = rightChild = task.makeChild(rs);task.setPendingCount(1);if (forkRight) {forkRight = false;rs = ls;task = leftChild;taskToFork = rightChild;}else {forkRight = true;task = rightChild;taskToFork = leftChild;}taskToFork.fork();sizeEstimate = rs.estimateSize();}task.setLocalResult(task.doLeaf());task.tryComplete();}
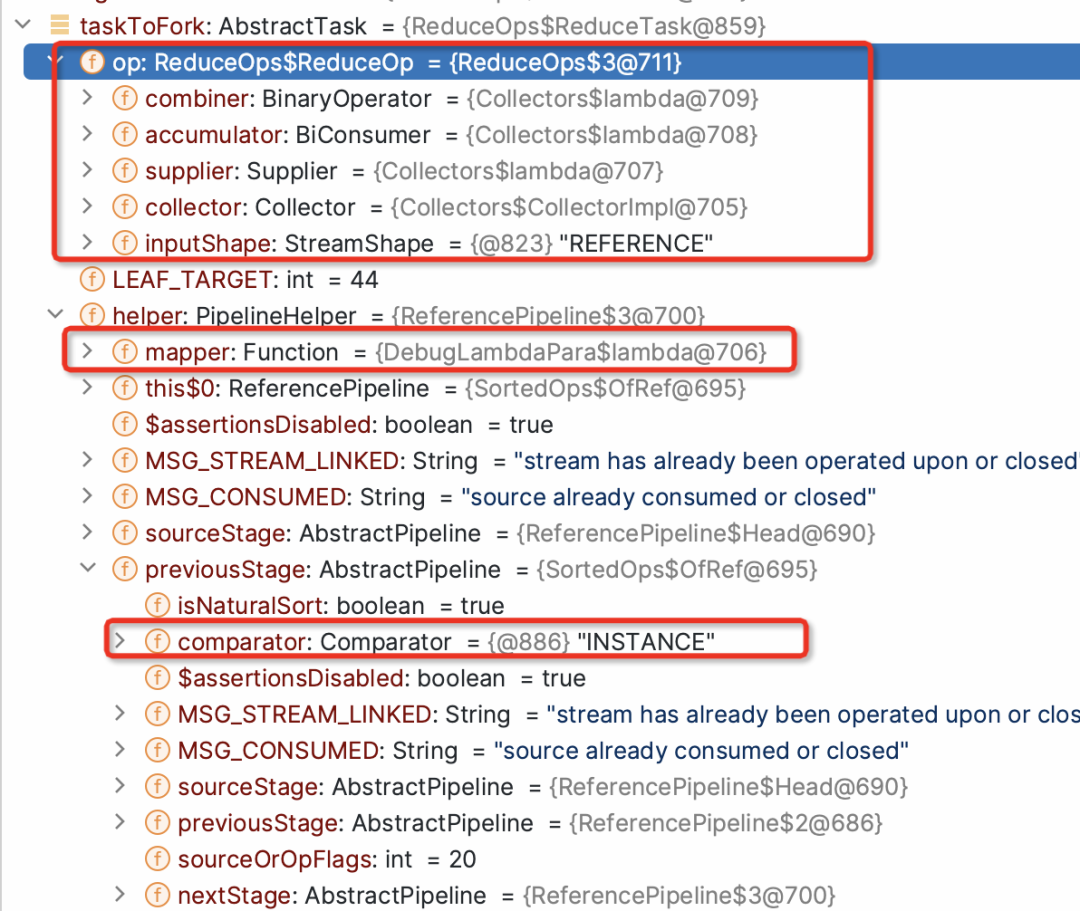
public final ForkJoinTask<V> fork() {Thread t;if ((t = Thread.currentThread()) instanceof ForkJoinWorkerThread)((ForkJoinWorkerThread)t).workQueue.push(this);elseForkJoinPool.common.externalPush(this);return this;}
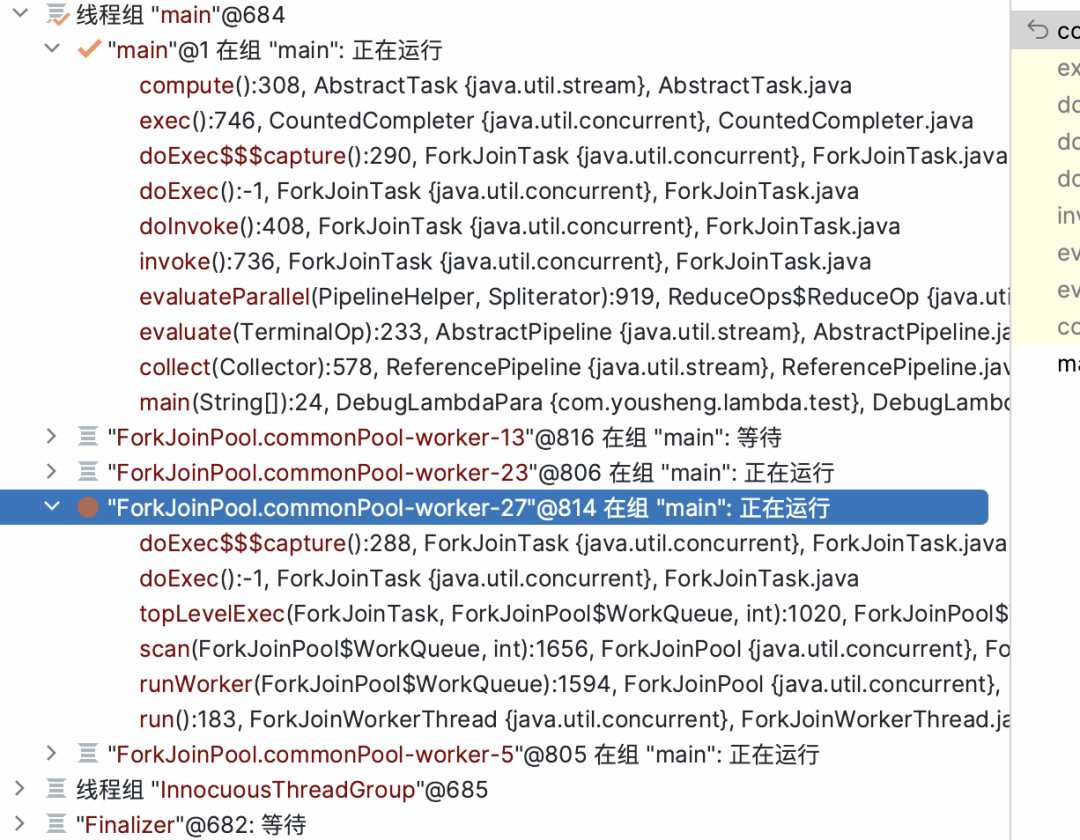
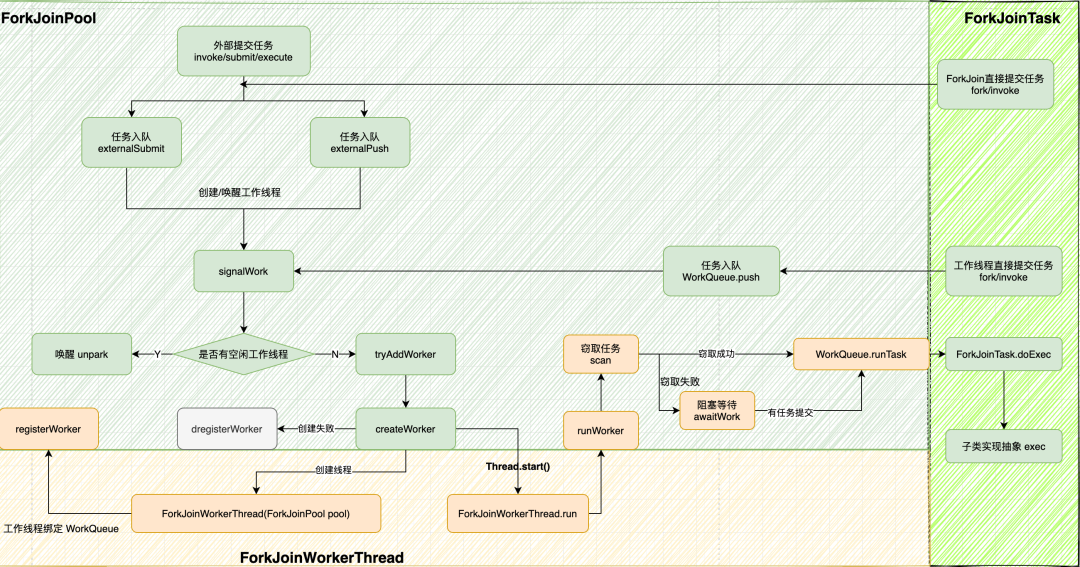
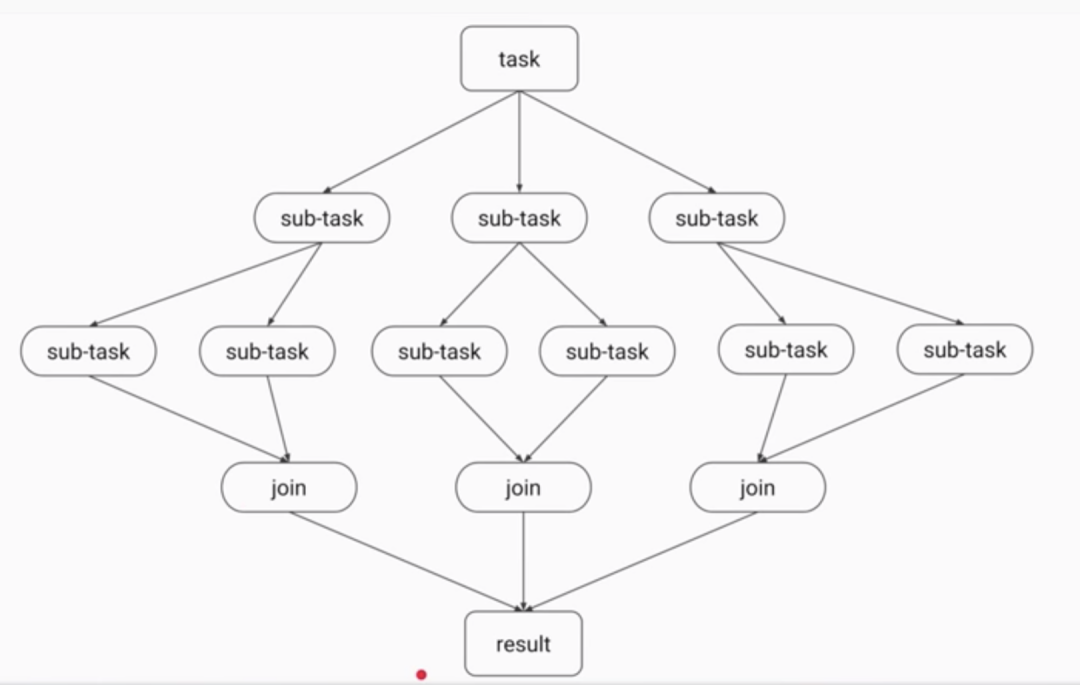
JVM分析
public static void main(String[] args) {Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).filter(x -> x > 2).forEach(System.out::println);}
0 iconst_51 anewarray #2 <java/lang/Integer>4 dup5 iconst_06 iconst_17 invokestatic #3 <java/lang/Integer.valueOf : (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;>10 aastore11 dup12 iconst_113 iconst_214 invokestatic #3 <java/lang/Integer.valueOf : (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;>17 aastore18 dup19 iconst_220 iconst_321 invokestatic #3 <java/lang/Integer.valueOf : (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;>24 aastore25 dup26 iconst_327 iconst_428 invokestatic #3 <java/lang/Integer.valueOf : (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;>31 aastore32 dup33 iconst_434 iconst_535 invokestatic #3 <java/lang/Integer.valueOf : (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;>38 aastore39 invokestatic #4 <java/util/stream/Stream.of : ([Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/util/stream/Stream;>42 invokedynamic #5 <test, BootstrapMethods #0>47 invokeinterface #6 <java/util/stream/Stream.filter : (Ljava/util/function/Predicate;)Ljava/util/stream/Stream;> count 252 getstatic #7 <java/lang/System.out : Ljava/io/PrintStream;>55 dup56 invokestatic #8 <java/util/Objects.requireNonNull : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;>59 pop60 invokedynamic #9 <accept, BootstrapMethods #1>65 invokeinterface #10 <java/util/stream/Stream.forEach : (Ljava/util/function/Consumer;)V> count 270 return
0 aload_01 invokevirtual #11 <java/lang/Integer.intValue : ()I>4 iconst_25 if_icmple 12 (+7)8 iconst_19 goto 13 (+4)12 iconst_013 ireturn





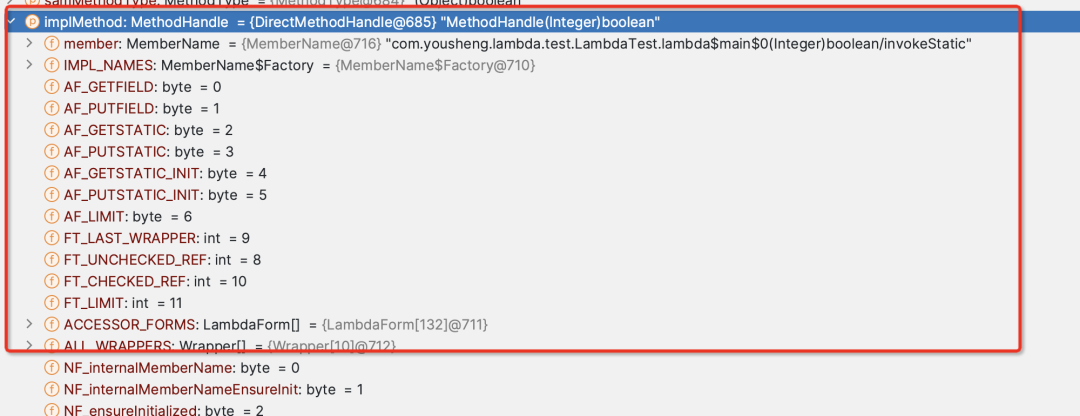
-
com.yousheng.lambda.test.LambdaTest — > 类名
-
lambda$main$0 — >类中的方法名称
-
(Integer)boolean — > 方法的描述符, (括号内的为入参类型,返回值为boolean)
-
invokeStatic –> 调用字节码。在jvm中有5中invoke字节码指令,分别为

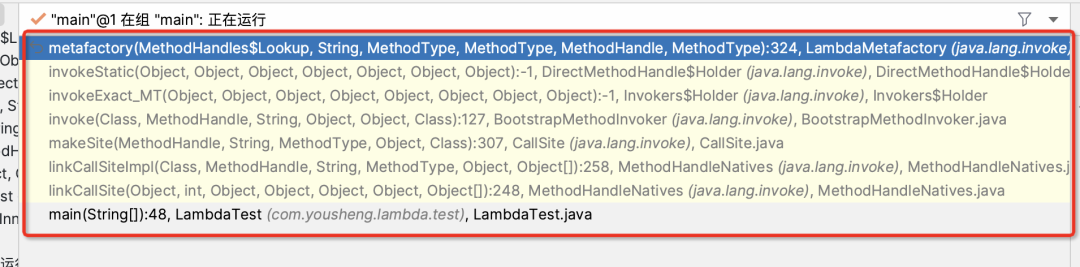
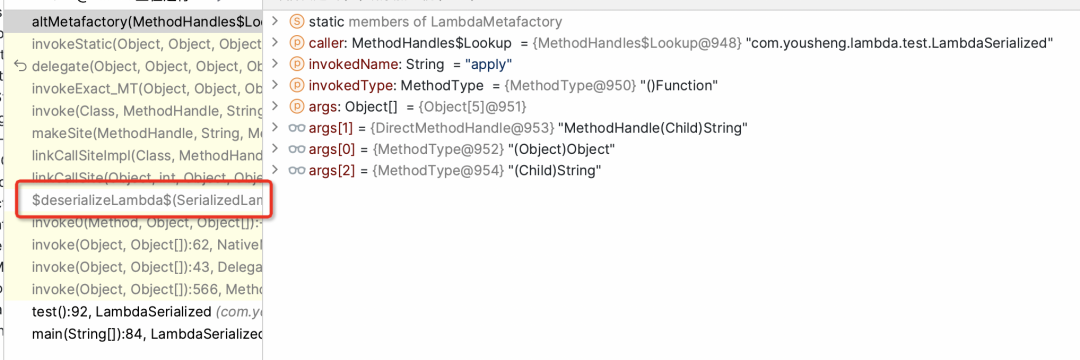
继续查看栈帧发现此方法是由Jvm调用而来,metafactory的上一个方法是invokeStatic当时行号是-1所以说明是jvm内部方法
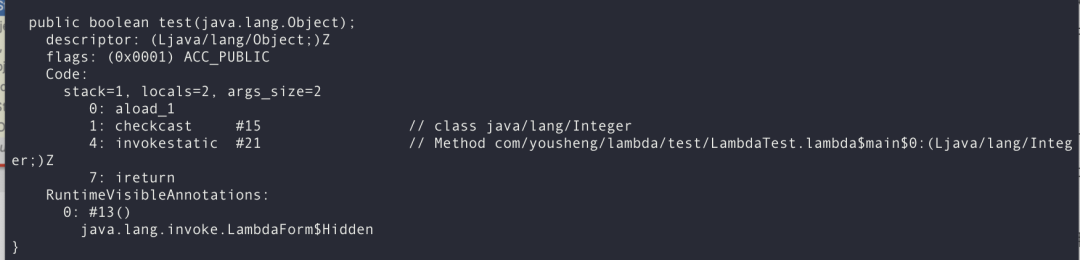



Lambda的序列化原理
final class LambdaTest$$Lambda$15 implements Function, Serializable {private LambdaTest$$Lambda$15() {}public Object apply(Object var1) {return ((Child)var1).getName();}private final Object writeReplace() {return new SerializedLambda(LambdaTest.class, "java/util/function/Function", "apply", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;", 5, "com/yousheng/lambda/entity/Child", "getName", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "(Lcom/yousheng/lambda/entity/Child;)Ljava/lang/String;", new Object[0]);}}
/*** Serialized form of a lambda expression. The properties of this class* represent the information that is present at the lambda factory site, including* static metafactory arguments such as the identity of the primary functional* interface method and the identity of the implementation method, as well as* dynamic metafactory arguments such as values captured from the lexical scope* at the time of lambda capture.** <p>Implementors of serializable lambdas, such as compilers or language* runtime libraries, are expected to ensure that instances deserialize properly.* One means to do so is to ensure that the {@code writeReplace} method returns* an instance of {@code SerializedLambda}, rather than allowing default* serialization to proceed.** <p>{@code SerializedLambda} has a {@code readResolve} method that looks for* a (possibly private) static method called* {@code $deserializeLambda$(SerializedLambda)} in the capturing class, invokes* that with itself as the first argument, and returns the result. Lambda classes* implementing {@code $deserializeLambda$} are responsible for validating* that the properties of the {@code SerializedLambda} are consistent with a* lambda actually captured by that class.** <p>The identity of a function object produced by deserializing the serialized* form is unpredictable, and therefore identity-sensitive operations (such as* reference equality, object locking, and {@code System.identityHashCode()} may* produce different results in different implementations, or even upon* different deserializations in the same implementation.** @see LambdaMetafactory* @since 1.8*/
0 aload_01 invokevirtual #28 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getImplMethodName : ()Ljava/lang/String;>4 astore_15 iconst_m16 istore_27 aload_18 invokevirtual #29 <java/lang/String.hashCode : ()I>11 lookupswitch 1: 28 (+17)default: 39 (+28)28 aload_129 ldc #14 <getName>31 invokevirtual #30 <java/lang/String.equals : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z>34 ifeq 39 (+5)37 iconst_038 istore_239 iload_240 lookupswitch 10: 60 (+20)default: 134 (+94)60 aload_061 invokevirtual #31 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getImplMethodKind : ()I>64 iconst_565 if_icmpne 134 (+69)68 aload_069 invokevirtual #32 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getFunctionalInterfaceClass : ()Ljava/lang/String;>72 ldc #33 <com/yousheng/lambda/test/Func>74 invokevirtual #34 <java/lang/Object.equals : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z>77 ifeq 134 (+57)80 aload_081 invokevirtual #35 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getFunctionalInterfaceMethodName : ()Ljava/lang/String;>84 ldc #11 <apply>86 invokevirtual #34 <java/lang/Object.equals : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z>89 ifeq 134 (+45)92 aload_093 invokevirtual #36 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getFunctionalInterfaceMethodSignature : ()Ljava/lang/String;>96 ldc #12 <(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;>98 invokevirtual #34 <java/lang/Object.equals : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z>101 ifeq 134 (+33)104 aload_0105 invokevirtual #37 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getImplClass : ()Ljava/lang/String;>108 ldc #13 <com/yousheng/lambda/entity/Child>110 invokevirtual #34 <java/lang/Object.equals : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z>113 ifeq 134 (+21)116 aload_0117 invokevirtual #38 <java/lang/invoke/SerializedLambda.getImplMethodSignature : ()Ljava/lang/String;>120 ldc #15 <()Ljava/lang/String;>122 invokevirtual #34 <java/lang/Object.equals : (Ljava/lang/Object;)Z>125 ifeq 134 (+9)128 invokedynamic #2 <apply, BootstrapMethods #0> // 注意133 areturn134 new #39 <java/lang/IllegalArgumentException>137 dup138 ldc #40 <Invalid lambda deserialization>140 invokespecial #41 <java/lang/IllegalArgumentException.<init> : (Ljava/lang/String;)V>143 athrow
private Object readResolve() throws ReflectiveOperationException {try {Method deserialize = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<>() {public Method run() throws Exception {Method m = capturingClass.getDeclaredMethod("$deserializeLambda$", SerializedLambda.class);m.setAccessible(true);return m;}});return deserialize.invoke(null, this);}catch (PrivilegedActionException e) {Exception cause = e.getException();if (cause instanceof ReflectiveOperationException)throw (ReflectiveOperationException) cause;else if (cause instanceof RuntimeException)throw (RuntimeException) cause;elsethrow new RuntimeException("Exception in SerializedLambda.readResolve", e);}}
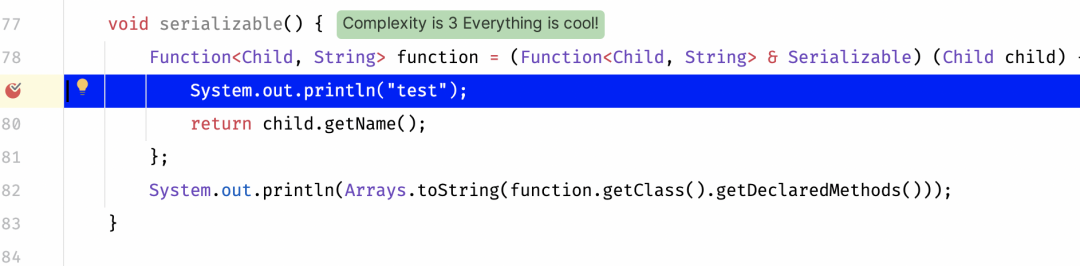
class LambdaSerialized {void serializable() {Function<Child, String> function = (Function<Child, String> & Serializable) (Child child) -> {System.out.println("test");return child.getName();};System.out.println(Arrays.toString(function.getClass().getDeclaredMethods()));}public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException {Child child = new Child("yousheng", 18);// 下方输出结果 youshengSystem.out.println(new LambdaSerialized().<Function<Child, String>>test().apply(child));}static <T> T test() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {SerializedLambda serializedLambda = new SerializedLambda(LambdaSerialized.class, "java/util/function/Function", "apply", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Ljava/lang/Object;", 5, "com/yousheng/lambda/entity/Child", "getName", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "(Lcom/yousheng/lambda/entity/Child;)Ljava/lang/String;", new Object[0]);Method m = Class.forName(serializedLambda.getCapturingClass().replace('/', '.')).getDeclaredMethod("$deserializeLambda$", SerializedLambda.class);m.setAccessible(true);return (T)m.invoke(null, serializedLambda);}}// Child类定义如下class Child {private String name;private int age;}
图计算及其应用
近年来,基于图数据的计算(图计算)得到了学术界和工业界越来越多的关注。本专场围绕图计算系统、应用及前沿学术研究问题,首先介绍阿里巴巴开源的一站式图计算系统 GraphScope的设计思想、基础能力以及未来发展方向;另外,邀请来自学术界和工业界的大咖,分享图计算最前沿的学术和技术热点;同时,邀请在业务中应用图计算技术的客户,分享图计算在真实业务场景中的应用案例。
点击阅读原文查看详情。
 微信赞赏
微信赞赏 支付宝扫码领红包
支付宝扫码领红包