接口请求合并技巧,用好了效率直接翻倍!
一、什么是请求合并
在WEB项目中,我们一般会使用HTTP协议来处理请求
那么我们与服务器交互方式将会是这样的,一次请求,一次处理
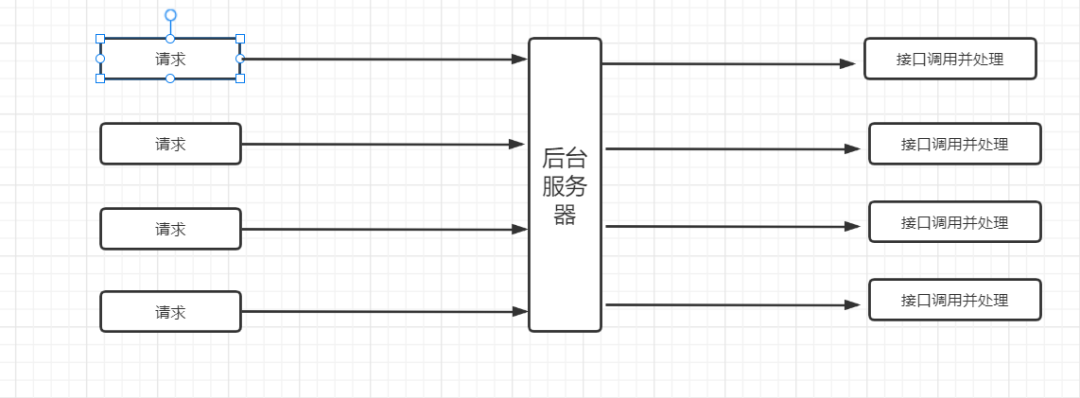
我们都知道,调用批量接口相比调用非批量接口有更大的性能优势(因为减少了IO交互操作),在高并发情况下,如果有非常频繁的接口请求发生的话,我们则可以考虑请求合并了,将多个请求进行一定的等待延迟,当请求累计达到一定量级的时候,进行批量请求处理
二、请求合并的优缺点
所谓请求合并,就是讲多次请求合并为一次批量请求
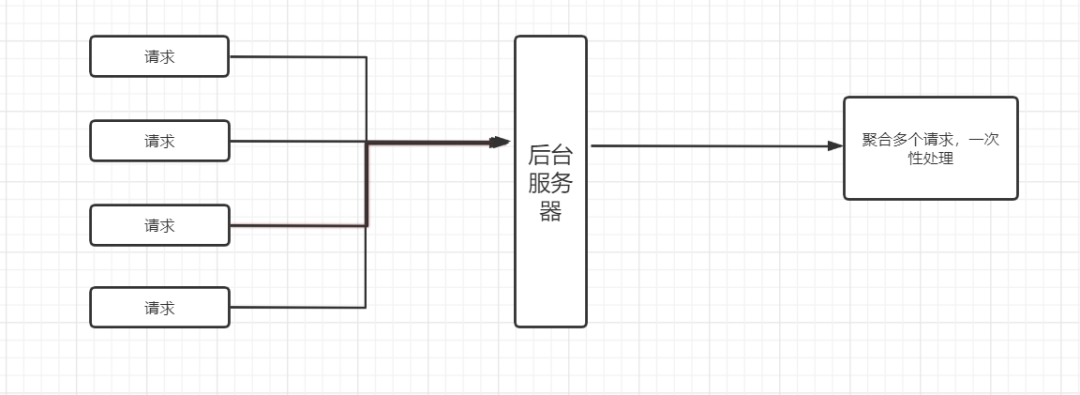
优点:
将多次请求处理进行一定时间或请求数量的等待,使之合并成为一次请求,减少IO交互
缺点:
由于请求需要等待指定时间或指定请求数量,所以合并的接口存在延时,故对请求合并的接口有所限制,该接口不能对响应及时性有要求,支持一定时间的延迟
三、请求合并技术实现
采用定时线程池ScheduledExecutorService,与内存队列LinkedBlockingDeque进行实现请求合并
❝原理是将用户的请求进行缓存起来,缓存的请求数量达到指定数量或达到定时线程池执行时,将已有多个单请求处理合并为多处理,调用批量接口进行操作
❞
依赖
-
只需要JDK,无需任何第三方依赖
批量请求合并工具类定义如下:
核心原理就是 将请求放入队列,放入时检测内存队列数量是否超过设置阈值,以及时间阈值到期触发定时线程池执行
package com.leilei.support;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @author lei
* @desc 请求合并工具类
**/
@Log4j2
public class BatchCollapser<T, R> {
private static final Map<Class, BatchCollapser> BATCH_INSTANCE =new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final ScheduledExecutorService SCHEDULE_EXECUTOR = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
private final LinkedBlockingDeque<T> batchContainer = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>();
private final BatchHandler<List<T>, R> handler;
private final int countThreshold;
/**
* constructor
*
* @param handler 处理器
* @param countThreshold 数量阈值,达到此阈值后触发处理器
* @param timeThreshold 时间阈值,达到此时间后触发处理器
*/
private BatchCollapser(BatchHandler<List<T>, R> handler, int countThreshold, long timeThreshold) {
this.handler = handler;
this.countThreshold = countThreshold;
SCHEDULE_EXECUTOR.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
this.popUpAndHandler(BatchHandlerType.BATCH_HANDLER_TYPE_TIME);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("pop-up container exception", e);
}
}, timeThreshold, timeThreshold, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 添加请求元素入队
* @param event
*/
public void addRequestParam(T event) {
batchContainer.add(event);
if (batchContainer.size() >= countThreshold) {
popUpAndHandler(BatchHandlerType.BATCH_HANDLER_TYPE_DATA);
}
}
/**
* 从队列获取请求,并进行批量处理
* @param handlerType
*/
private void popUpAndHandler(BatchHandlerType handlerType) {
List<T> tryHandlerList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>(countThreshold));
batchContainer.drainTo(tryHandlerList, countThreshold);
if (tryHandlerList.size() < 1) {
return;
}
try {
R handle = handler.handle(tryHandlerList, handlerType);
log.info("批处理工具执行result:{}", handle);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("batch execute error, transferList:{}", tryHandlerList, e);
}
}
/**
* 获取合并器实例
*
* @param batchHandler 处理执行器
* @param countThreshold 阈值数量(队列数量)
* @param timeThreshold 阈值时间 单位秒(目前设置是触发后获取阈值数量请求,可根据需要修改)
* @param <E>
* @param <R>
* @return
*/
public static <E, R> BatchCollapser<E, R> getInstance(BatchHandler<List<E>, R> batchHandler, int countThreshold, long timeThreshold) {
Class jobClass = batchHandler.getClass();
if (BATCH_INSTANCE.get(jobClass) == null) {
synchronized (BatchCollapser.class) {
BATCH_INSTANCE.putIfAbsent(jobClass, new BatchCollapser<>(batchHandler, countThreshold, timeThreshold));
}
}
return BATCH_INSTANCE.get(jobClass);
}
/**
* 请求处理接口
*
* @param <T>
* @param <R>
*/
public interface BatchHandler<T, R> {
/**
* 处理用户具体请求
*
* @param input
* @param handlerType
* @return
*/
R handle(T input, BatchHandlerType handlerType);
}
/**
* 合并执行类型枚举
*/
public enum BatchHandlerType {
/**
* 数量类型
*/
BATCH_HANDLER_TYPE_DATA,
/**
* 时间类型
*/
BATCH_HANDLER_TYPE_TIME,
}
}
使用方式如下:
package com.leilei.support;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author lei
* @desc
**/
@Service
public class ProductService implements BatchCollapser.BatchHandler<List<Integer>, Integer> {
private BatchCollapser<Integer, Integer> batchCollapser;
@PostConstruct
private void postConstructorInit() {
// 当请求数量达到20个,或每过5s合并执行一次请求
batchCollapser = BatchCollapser.getInstance(ProductService.this, 20, 5);
}
@Override
public Integer handle(List<Integer> input, BatchCollapser.BatchHandlerType handlerType) {
System.out.println("处理类型:" + handlerType + ",接受到批量请求参数:" + input);
return input.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).sum();
}
/**
* 假设我这里是300ms一次请求
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 300)
public void aaa() {
Integer requestParam = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;
batchCollapser.addRequestParam(requestParam);
System.out.println("当前请求参数:" + requestParam);
}
}
@Data
public class Product {
private Integer id;
private String notes;
}
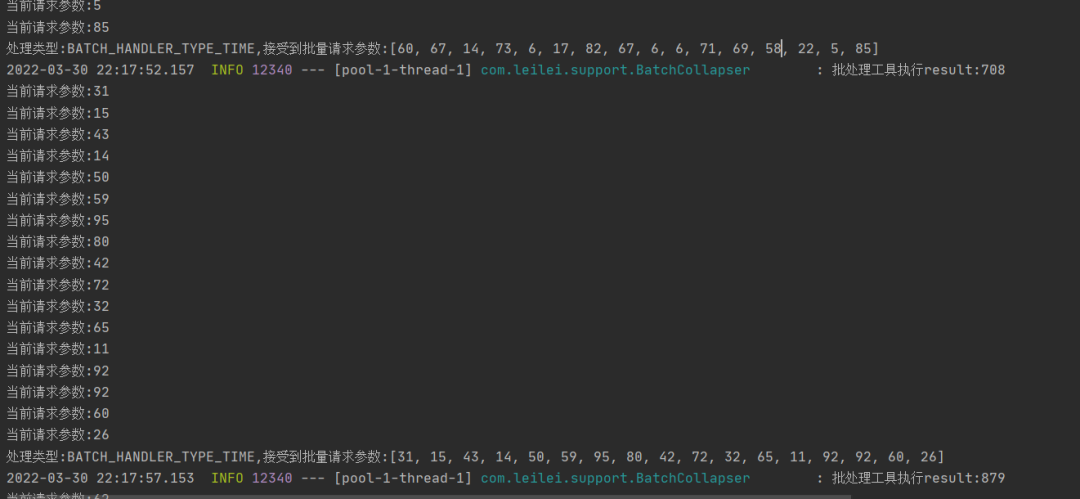
当然以上工具类仅仅只是DEMO,各位大佬可自行完善,权衡请求合并利弊,降低服务器在高并发请求时的压力
扫码领红包 微信赞赏
微信赞赏 支付宝扫码领红包
支付宝扫码领红包
声明:本站所有文章,如无特殊说明或标注,均为本站原创发布。任何个人或组织,在未征得本站同意时,禁止复制、盗用、采集、发布本站内容到任何网站、书籍等各类媒体平台。如若本站内容侵犯了原著者的合法权益,可联系我们进行处理。侵权投诉:375170667@qq.com