语法详解
字面量表达式
SpEL 支持以下字面量表达式:
-
字符串 (String) -
数值: 整数 int or long 类型,十六进制 int or long 类型以及浮点类型 float or double -
布尔值: true or false -
空对象 : null
示例:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 8:46 PM
* @Description:
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class LiteralExpressions {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// 解析 字符串
String value = parser.parseExpression("'Hello,Literal Expression'").getValue(String.class);
System.out.println(value);
// 解析 数值 int long float double
double number = parser.parseExpression("4.5").getValue(double.class);
System.out.println(number);
// 解析 布尔值 true or false
boolean bool = parser.parseExpression("true").getValue(boolean.class);
System.out.println(bool);
// 解析 空对象 null
Object obj = parser.parseExpression("null").getValue();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
执行结果:

属性表达式
在 SpEL 表达式中,我们可以通过 属性名 来获取对应路径的内容,如果涉及到嵌套属性,我们用 ‘.’ 来表示级联关系。
示例:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 8:59 PM
* @Description:
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class PropertiesExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Inventor inventor = InventorBuilder.builder();
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(inventor);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String name = parser.parseExpression("name").getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(name);
// nested property
int length = parser.parseExpression("name.length").getValue(context, int.class);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
执行结果:

容器表达式
这里的容器用于表示 数组(Array)、集合(List)、字典(Map),我们统一来看下有关于这些内容的 SpEL 表达式都有哪些
Array
-
索引获取,通过方括号[index]来获取目标索引值 -
数组构造,包括基本类型构造、复杂类型构造
示例:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 9:10 PM
* @Description: 数组相关的表达式示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class ArraysExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// array
Inventor[] inventors = {InventorBuilder.builder()};
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(inventors);
// index 表达
Inventor inventor = parser.parseExpression("[0]").getValue(context, Inventor.class);
System.out.println(inventor);
// index + nested property
String name = parser.parseExpression("[0].name").getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(name);
// index + nested property index
inventor.getBooleans().add(true);
boolean bool = parser.parseExpression("[0].booleans[0]").getValue(context, boolean.class);
System.out.println(bool);
// array construction
int[] numbers = parser.parseExpression("new int[]{1,2,3}").getValue(context, int[].class);
for (int number : numbers) {
System.out.print(number + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// complex type arrays constructor
Inventor[] complexTypeArrays = parser
.parseExpression("new com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor[1]")
.getValue(context, Inventor[].class);
complexTypeArrays[0] = InventorBuilder.builder();
Arrays.stream(complexTypeArrays).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
List
集合和数组的数据访问以及嵌套属性访问的方式一致,示例可以参考 Array 实现。我们额外补充些有关 List 的示例
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 9:32 PM
* @Description: List 集合有关 SpEL 表达式的示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class ListExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Inventor inventor = InventorBuilder.builder();
List<Inventor> inventors = new ArrayList<>();
inventors.add(inventor);
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(inventors);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// by [index] get element
Inventor inventorFromParser = parser.parseExpression("[0]").getValue(context, Inventor.class);
System.out.println(inventorFromParser);
// inline list
// 1. simple type
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Integer> integers = parser.parseExpression("{1,2,3,4,5}").getValue(context, List.class);
System.out.println(integers);
// 2. complex type
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Inventor> inventorList = (List<Inventor>) parser.parseExpression("{T(com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder).builder()}").getValue(context);
System.out.println(inventorList);
}
}
执行结果:
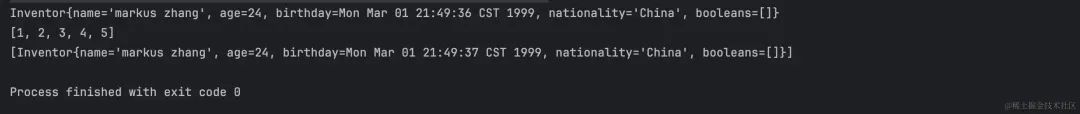
Map
Map中的数据访问有些不同,示例如下所示:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 9:47 PM
* @Description:
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class MapExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Inventor inventor = InventorBuilder.builder();
Map<String, Inventor> map = new HashMap();
map.put("markus", inventor);
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext(map);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// by ['key'] get element
Inventor inventorFromParser = parser.parseExpression("['markus']").getValue(context, Inventor.class);
System.out.println(inventorFromParser);
// nested property access
String name = parser.parseExpression("['markus'].name").getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(name);
// inline map
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<String, Inventor> inventorMap = parser
.parseExpression("{'markus':T(com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder).builder()}")
.getValue(context, Map.class);
System.out.println(inventorMap);
}
}
执行结果:
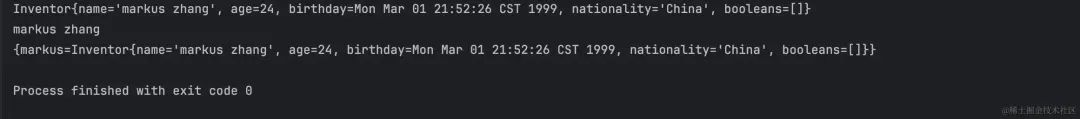
方法调用表达式
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 9:55 PM
* @Description: 方法调用表达式的示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class MethodInvokeExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String subString = parser.parseExpression("'Hello,SpEL'.substring(0,5)").getValue(String.class);
System.out.println(subString);
}
}
执行结果:

运算符表达式
SpEL 表达式支持如下运算法:
-
关系运算符 -
逻辑运算符 -
算术运算符 -
赋值运算符
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 10:00 PM
* @Description: 运算符 SpEL 示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class OperatorsExpression {
/**
* more demo please reference https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/core/expressions/language-ref/operators.html
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// first : relational operators
boolean result = parser.parseExpression("2 < 5").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("2 < 5 : " + result);
result = parser.parseExpression("2 == 5").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("2 == 5 : " + result);
result = parser.parseExpression("1 instanceof T(int)").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("1 instanceof T(int) : " + result);
result = parser.parseExpression("1 instanceof T(Integer)").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("1 instanceof T(Integer) : " + result);
// second : logical operators
// and (&&)
// or (||)
// not (!)
result = parser.parseExpression("true or false").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("true or false : " + result);
result = parser.parseExpression("true and false").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("true and false : " + result);
result = parser.parseExpression("!true").getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println("!true : " + result);
// third : mathematical operators
// + - * / %
// Addition
int two = parser.parseExpression("1 + 1").getValue(Integer.class); // 2
System.out.println("1 + 1 : " + two);
String testString = parser.parseExpression(
"'test' + ' ' + 'string'").getValue(String.class); // 'test string'
System.out.println("'test' + ' ' + 'string' : " + testString);
// Subtraction
int four = parser.parseExpression("1 - -3").getValue(Integer.class); // 4
System.out.println("1 - -3 : " + four);
double d = parser.parseExpression("1000.00 - 1e4").getValue(Double.class); // -9000
System.out.println("1000.00 - 1e4 : " + d);
// Multiplication
int six = parser.parseExpression("-2 * -3").getValue(Integer.class); // 6
System.out.println("-2 * -3 : " + six);
double twentyFour = parser.parseExpression("2.0 * 3e0 * 4").getValue(Double.class); // 24.0
System.out.println("2.0 * 3e0 * 4 : " + twentyFour);
// Division
int minusTwo = parser.parseExpression("6 / -3").getValue(Integer.class); // -2
System.out.println("6 / -3 : " + minusTwo);
double oneD = parser.parseExpression("8.0 / 4e0 / 2").getValue(Double.class); // 1.0
System.out.println("8.0 / 4e0 / 2 : " + oneD);
// Modulus
int three = parser.parseExpression("7 % 4").getValue(Integer.class); // 3
System.out.println("7 % 4 : " + three);
int one = parser.parseExpression("8 / 5 % 2").getValue(Integer.class); // 1
System.out.println("8 / 5 % 2 : " + one);
// Operator precedence
int minusTwentyOne = parser.parseExpression("1+2-3*8").getValue(Integer.class); // -21
System.out.println("1+2-3*8 : " + minusTwentyOne);
}
}
执行结果:

类型表达式
我们可以通过 T(xxx) 来表示 Class 的实例,静态方法也可以通过这个方式使用,前面我们已经展示过,即 T(xxx).method(xxx),另外值得注意的是,在java.lang包下的类可以不指定全限定名,直接指定类名。
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 10:25 PM
* @Description: 类型 相关的 SpEL 示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class TypeExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Class dateClass = parser.parseExpression("T(java.util.Date)").getValue(Class.class);
System.out.println(dateClass);
Class stringClass = parser.parseExpression("T(String)").getValue(Class.class);
System.out.println(stringClass);
boolean trueValue = parser.parseExpression(
"T(java.math.RoundingMode).CEILING < T(java.math.RoundingMode).FLOOR")
.getValue(Boolean.class);
System.out.println(trueValue);
}
}
执行结果:

构造器表达式
通过 SpEL 来初始化实例,使用时必须要指定全限定名(包括 java.lang 包下的)
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 10:31 PM
* @Description: 构造器 SpEL 示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class ConstructorExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Inventor einstein = parser.parseExpression(
"new com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor()")
.getValue(Inventor.class);
System.out.println(einstein);
}
}
执行结果:
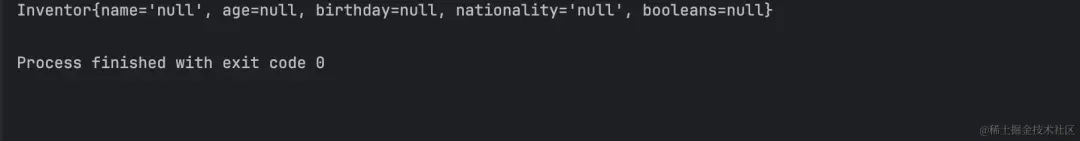
变量表达式
我们可以在 SpEL 中通过使用 #variableName 来获取执行的变量值。另外 变量的表示形式必须按照以下要求(至少有以下1个组成):
-
A-Z和a-z -
0-9 -
_ -
$
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.SimpleEvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 10:35 PM
* @Description: 变量 SpEL 表达式示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class VariableExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Inventor inventor = InventorBuilder.builder();
inventor.getBooleans().add(true);
inventor.getBooleans().add(false);
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadWriteDataBinding().build();
context.setVariable("newName", "Luna");
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
parser.parseExpression("name = #newName").getValue(context, inventor);
System.out.println(inventor);
// #this and #root
// #this 总是指向当前表达式中计算的对象
// #root 总是指向根对象
List<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>();
integers.add(1);
integers.add(2);
integers.add(3);
integers.add(4);
integers.add(5);
integers.add(6);
context.setVariable("integers", integers);
String thisExpression = "#integers.?[#this > 3]";
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Integer> gt3List = parser.parseExpression(thisExpression).getValue(context, List.class);
gt3List.forEach(integer -> System.out.print(integer + " "));
System.out.println();
// #root
context = new StandardEvaluationContext(inventor);
Inventor value = parser.parseExpression("#root").getValue(context, Inventor.class);
System.out.println(value);
}
}
执行结果:
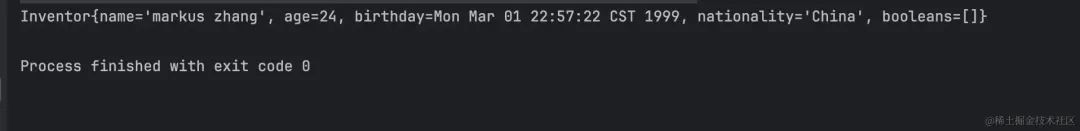
Bean 引用表达式
通过 @xxx 来获取 Spring 容器中的 Bean 实例
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import org.springframework.context.expression.BeanFactoryResolver;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 11:00 PM
* @Description: Bean 应用示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class BeanReferenceExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/META-INF/expression-in-bean-definitions.xml");
BeanFactoryResolver beanFactoryResolver = new BeanFactoryResolver(context.getBeanFactory());
StandardEvaluationContext evaluationContext = new StandardEvaluationContext();
evaluationContext.setBeanResolver(beanFactoryResolver);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String expression = "@inventor";
Inventor inventor = parser.parseExpression(expression).getValue(evaluationContext, Inventor.class);
System.out.println(inventor);
}
}
执行结果:

三元表达式
我们还可以在表达式内部使用三元运算符执行if-then-else条件逻辑。
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 11:07 PM
* @Description: 三元表达式 示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class TernaryOperatorExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
String falseString = parser.parseExpression(
"false ? 'trueExp' : 'falseExp'").getValue(String.class);
System.out.println("false ? 'trueExp' : 'falseExp' : " + falseString);
// The Elvis operator (精简版 三元表达式)
String name = parser.parseExpression("name?:'Unknown'").getValue(new Inventor(), String.class);
System.out.println(name); // 'Unknown'
}
}
执行结果:

安全指针表达式
为避免出现空指针,我们还可以在 SpEL 中使用 ?.来实现
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.SimpleEvaluationContext;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 11:11 PM
* @Description: 安全指针示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class SafeNavigationOperators {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();
Inventor inventor = new Inventor();
inventor.setName("markus zhang");
context.setVariable("inventor", inventor);
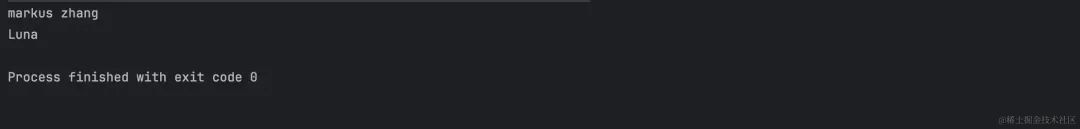
String name = parser.parseExpression("#inventor.name?.#inventor.name").getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(name); // markus zhang
inventor.setName(null);
name = parser.parseExpression("#inventor.name?.#inventor.name").getValue(context, String.class);
System.out.println(name); // null - does not throw NullPointerException!!!
}
}
执行结果:

集合筛选表达式
Selection是一种强大的表达语言功能,它允许您通过从其条目中进行选择,将源集合转换为另一个集合。选择使用的语法是.?[selectionExpression]。它过滤集合并返回一个包含原始元素子集的新集合。
示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 11:17 PM
* @Description: 集合元素选择 示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class CollectionSelectionExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
List<Integer> integers = new ArrayList<>();
integers.add(1);
integers.add(2);
integers.add(3);
integers.add(4);
integers.add(5);
integers.add(6);
context.setVariable("integers", integers);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Integer> list = (List<Integer>) parser.parseExpression(
"#integers.?[#this == 3 || #this == 4]").getValue(context);
list.forEach(ele -> {
System.out.print(ele + " ");
});
}
}
执行结果:

集合子集表达式
集合子集 意为 获取目标集合中某一字段集合,示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.Inventor;
import com.markus.spring.expression.language.InventorBuilder;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 11:17 PM
* @Description: 集合元素选择 示例
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class CollectionProjectionExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
List<Inventor> inventors = new ArrayList<>();
inventors.add(InventorBuilder.builder());
inventors.add(InventorBuilder.builder("Luna"));
context.setVariable("inventors", inventors);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<String> list = (List<String>) parser.parseExpression(
"#inventors.![name]").getValue(context);
list.forEach(ele -> {
System.out.println(ele + " ");
});
}
}
执行结果:
模板表达式
表达式执行一个模板,并在这个模板中通过 #{} 来占位,示例如下:
package com.markus.spring.expression.language.reference;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.ParserContext;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
/**
* @author: markus
* @date: 2024/1/21 11:29 PM
* @Description:
* @Blog: https://markuszhang.com
* It's my honor to share what I've learned with you!
*/
public class TemplateExpression {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
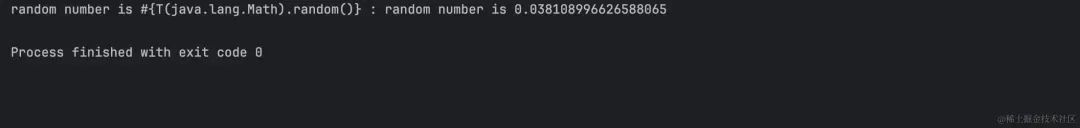
String randomPhrase = parser.parseExpression(
"random number is #{T(java.lang.Math).random()}",
new TemplateParserContext()).getValue(String.class);
System.out.println("random number is #{T(java.lang.Math).random()} : " + randomPhrase);
}
public static class TemplateParserContext implements ParserContext {
public String getExpressionPrefix() {
return "#{";
}
public String getExpressionSuffix() {
return "}";
}
public boolean isTemplate() {
return true;
}
}
}
执行结果:
本文总结
通过本文,我们详细讨论了 SpEL 的语法、特性和应用场景。从简单的字面量表达式到复杂的类型引用,相信大家已经掌握了在 Spring 项目中灵活使用 SpEL 的关键知识。
在总结中,不要忘记不断实践和深入研究,以便更好地运用 SpEL 提高代码的可读性和可维护性。感谢您的阅读,希望大家在今后的项目中充分发挥 SpEL 的潜力!
扫码领红包 微信赞赏
微信赞赏 支付宝扫码领红包
支付宝扫码领红包